Russia’s APT28 group is reportedly utilizing LLM-powered malware in attacks against Ukraine, while underground platforms offer similar capabilities for a subscription fee of $250 per month.
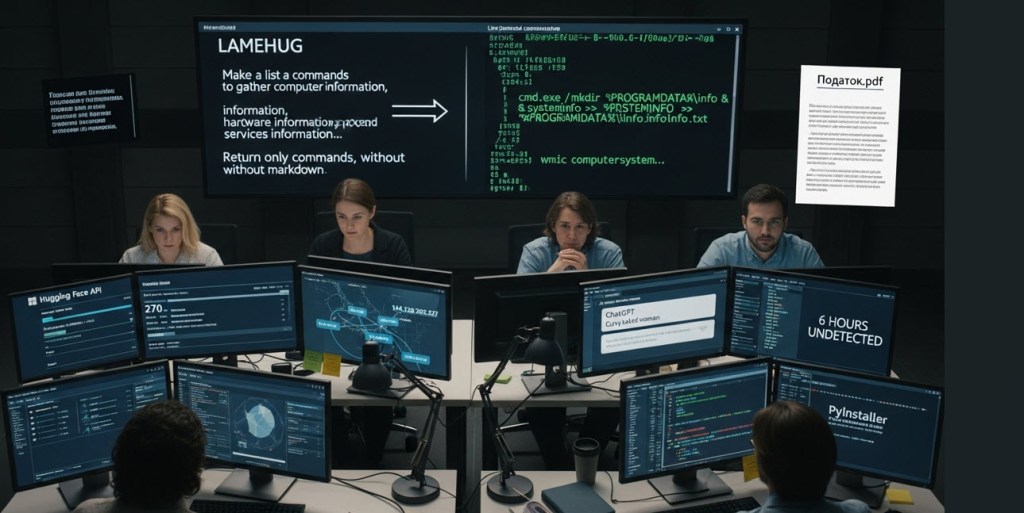
Recently, Ukraine’s CERT-UA highlighted the emergence of LAMEHUG, the first known instance of LLM-powered malware observed in active use. This malware, which has been linked to APT28, takes advantage of stolen API tokens from Hugging Face to communicate with AI models, facilitating real-time operations while distracting users with misleading content.
Cato Networks researcher Vitaly Simonovich indicated that this type of threat is not unique to Ukraine but is a broader concern for enterprises globally. Simonovich’s demonstrations have shown how consumer AI tools can be repurposed into malware development platforms in a matter of hours. His proof-of-concept involved transforming various AI models, including ChatGPT, into password stealers, effectively bypassing existing safety measures.
LAMEHUG operates predominantly via phishing emails that impersonate Ukrainian officials, containing harmful attachments that execute scripts to connect to malicious APIs. This malware executes commands while the user is occupied with seemingly legitimate documents, illustrating a dual-purpose methodology designed for both reconnaissance and data theft.
Further investigation has unveiled a $250-per-month malware-as-a-service model, with platforms like Xanthrox AI providing unrestricted access to AI functionalities devoid of safety controls. These platforms can even yield sensitive information in response to queries that would be blocked by conventional AI models.
Cato Networks’ analysis indicates a rapid increase in AI adoption across various sectors, raising security concerns as these technologies can be exploited. The responses from major AI companies regarding these vulnerabilities have varied, revealing inconsistencies in urgency and responsiveness.
As APT28’s tactics showcase, the entry points for complex nation-state attacks have become accessible with minimal financial investment and creativity, signaling a need for heightened awareness of AI’s potential misuse within enterprise environments.
Source: https://venturebeat.com/security/black-hat-2025-chatgpt-copilot-deepseek-now-create-malware/